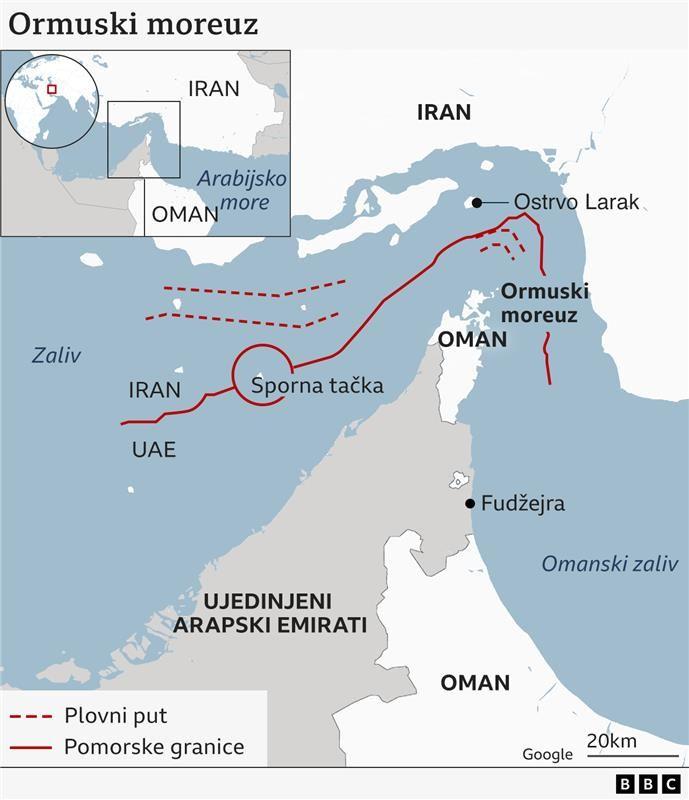
The conflict between Israel and Iran has led to a sharp increase in crude oil prices on the global market, raising concerns about rising energy costs and the potential increase in prices of essential goods such as gasoline and food. Although oil prices have risen by about $10 per barrel compared to the previous month, they remain significantly below the peak reached after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Experts note that the further development of the situation will depend on the duration of the conflict, involvement of other countries, and the possible closure of the Strait of Hormuz, a key route for global oil production. Increased energy prices affect agriculture, transportation, and food production, which may have long-term consequences for the global economy. However, if there are no supply disruptions, oil prices may stabilize. This conflict represents an additional shock to the already fragile global economic order, with potential impacts on inflation and monetary policy in developed countries.
Political Perspectives:
Left: Left-leaning sources emphasize the geopolitical instability caused by the Israel-Iran conflict and its impact on global energy markets, highlighting the risks to ordinary people through rising prices of fuel and food. They often stress the need for diplomatic solutions and criticize military interventions that exacerbate economic hardships globally.
Center: Center-leaning reports focus on the factual economic impact of the conflict on oil prices and the global economy, providing balanced analysis of market reactions and expert opinions. They highlight the uncertainty in the region and the potential scenarios affecting supply routes like the Strait of Hormuz, while noting the current prices remain below previous peaks.
Right: Right-leaning narratives tend to emphasize the strategic importance of the Middle East in global energy security and the potential threats posed by Iran’s actions. They may stress the need for strong defense policies and support for allies like Israel, while warning about the economic consequences of prolonged conflict and disruptions in oil supply.