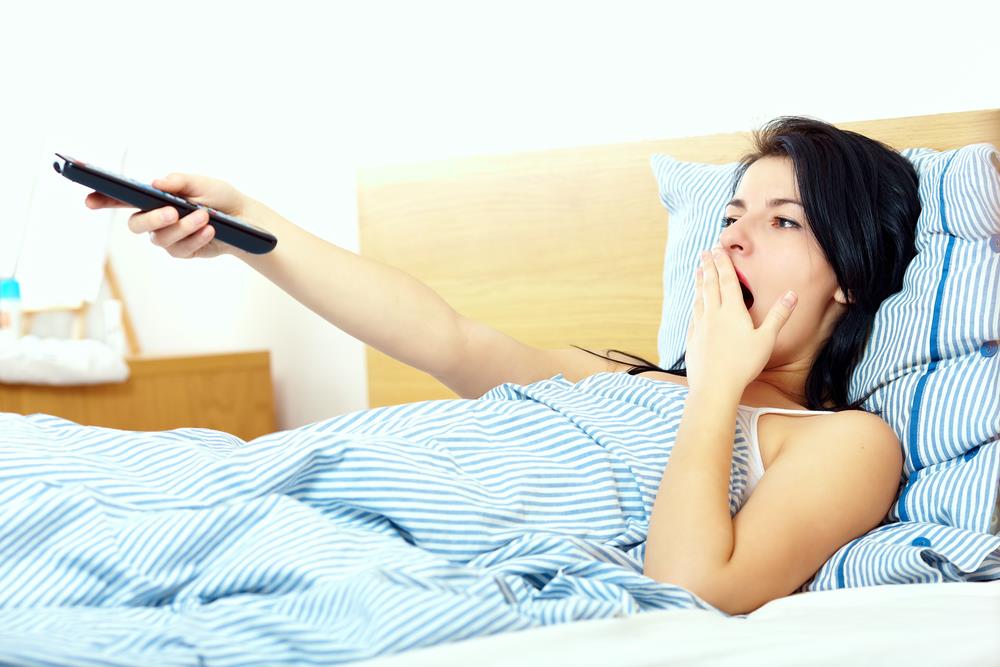
Sleeping with the TV on can negatively affect sleep quality and health. Research shows that the blue light emitted by the TV disrupts the production of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep, which can make falling asleep harder and reduce the REM sleep phase, crucial for body regeneration. Additionally, the noise and light from the TV can cause irritability, anxiety, and increase the risk of heart problems, high blood pressure, and weight gain. While some find the background noise of the TV soothing, experts recommend using alternative sounds like ambient music for better sleep hygiene. It is advised to gradually reduce dependence on the TV for falling asleep to improve sleep quality and overall health.
Political Perspectives:
Left: Left-leaning sources emphasize the health risks associated with sleeping with the TV on, focusing on the scientific research about melatonin disruption, anxiety, and long-term health consequences such as heart disease and obesity. They often advocate for better sleep hygiene and alternatives to TV noise, highlighting the importance of mental and physical well-being.
Center: Center-leaning sources present a balanced view, acknowledging both the potential negative effects of sleeping with the TV on and the subjective comfort it may provide to some individuals. They tend to focus on practical advice, such as gradually reducing TV use before sleep and suggesting alternative soothing sounds, without strongly emphasizing health risks or benefits.
Right: Right-leaning sources may downplay the health risks, sometimes highlighting personal choice and comfort. They might emphasize that for some people, the TV provides a sense of security and helps them fall asleep, suggesting that the issue is more about individual habits rather than a widespread health concern. They may also be skeptical of over-medicalizing everyday behaviors.